|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
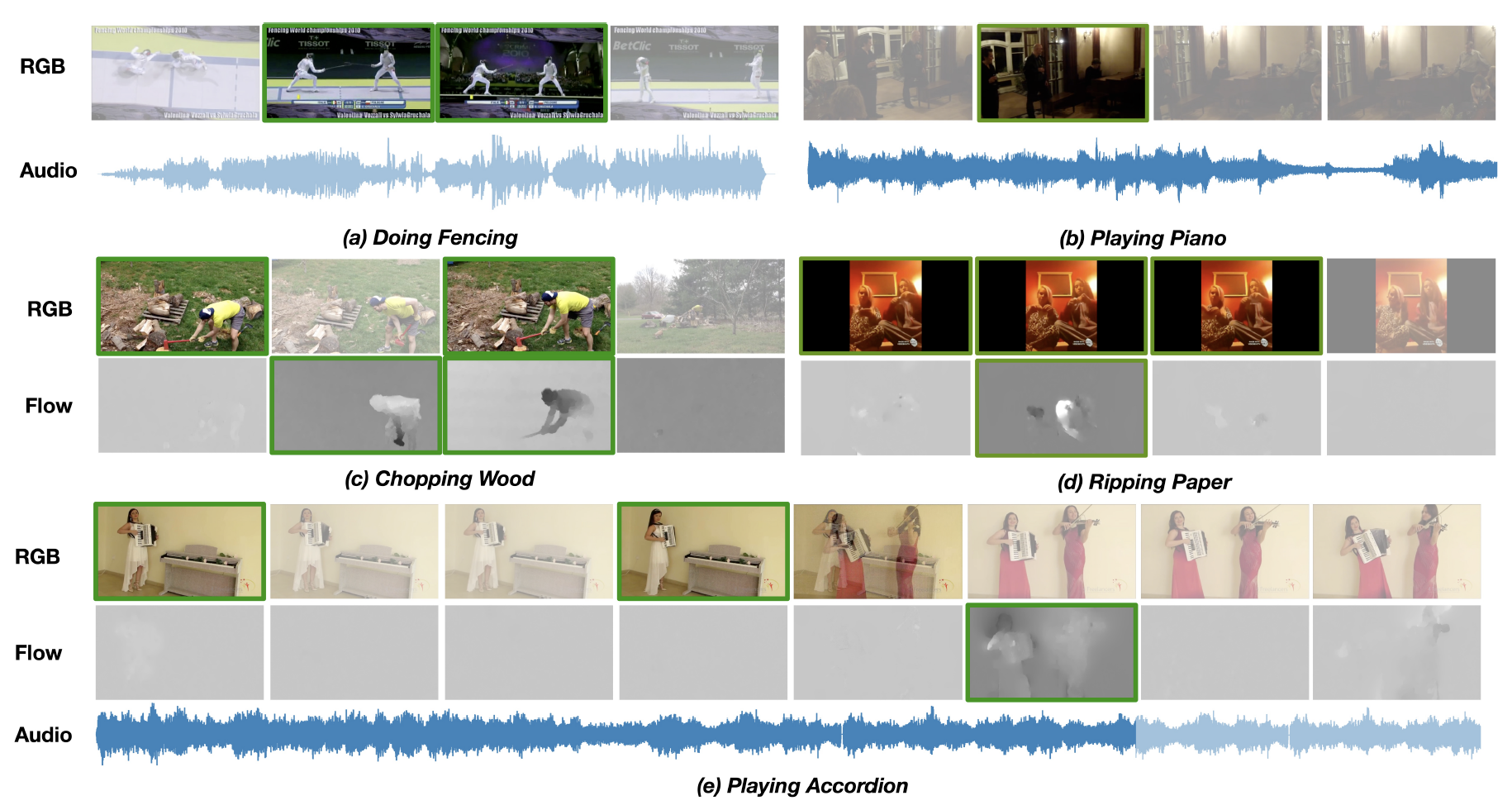 |

|
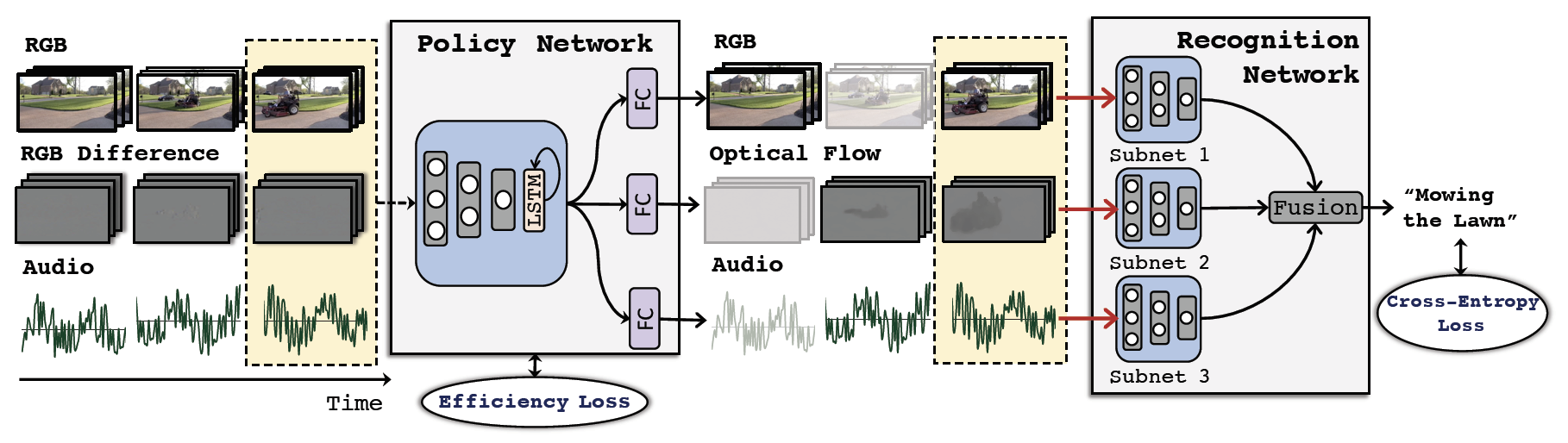
Rameswar Panda*, Chun-Fu (Richard) Chen*, Quanfu Fan, Ximeng Sun, Kate Saenko, Aude Oliva, Rogerio Feris AdaMML: Adaptive Multi-Modal Learning for Efficient Video Recognition International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2021 [PDF] [Supp] [Poster] [Slides] [Code] |